A common sleep problem affecting millions of people is sleep apnea. It stops breathing during sleep. These pauses could run a few seconds to several minutes. Many nights, they can occur numerous times. Sleep apnea disturbs sleep and might cause major medical problems. Those suffering from this disorder can snore loudly. Even after a full night's sleep, they could feel weary during the day.
Though there are other forms of sleep apnea, obstructive sleep apnea is the most common one. Correct therapy and management depend on awareness of sleep apnea. This guide will discuss the causes, symptoms, risk factors, diagnosis, and treatment choices for sleep apnea. Knowing more about this disorder can help you take action to enhance your general health and quality of sleep.
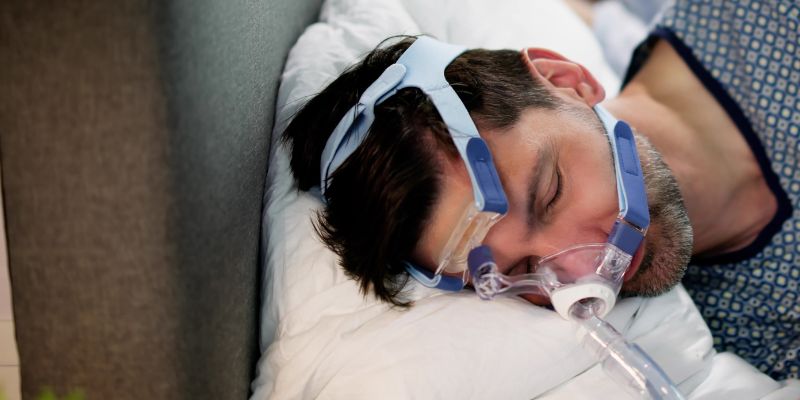
What is Sleep Apnea?
Sleep apnea is a major sleep condition marked by recurrent disruptions in breathing during sleep. These breathing pauses could happen several times a night and last a few seconds to minutes. Often, the body wakes up momentarily to start breathing when it pauses. This results in fragmented sleep, which fuels too much daytime tiredness and sleepiness.
Many people with sleep apnea may not remember waking up during the night, so they are ignorant that they have the disorder. Rather, family members sometimes observe symptoms such as loud snoring or dyspnea for air. Understanding these symptoms is vital, as untreated sleep apnea can cause major medical problems like heart disease and diminished cognitive ability.
Types of Sleep Apnea
Three basic forms of sleep apnea exist: obstructive, central, and complicated.
- Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA): Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) is the most common occurrence. It results from too-relaxed throat muscles during sleep. Relaxation like this blocks the airway. Those with OSA might choke or snore loudly while asleep.
- Central Sleep Apnea (CSA) results from a brain failing to send messages to the muscles controlling respiration. A closed airway like OSA does not cause CSA, but it can result from some medical illnesses.
- Complex Sleep Apnea Syndrome: Complex sleep apnea syndrome comprises central and obstructive sleep apnea. Those with this disorder may exhibit traits of both categories, which would complicate diagnosis and therapy.
Sleep Apnea Symptoms
Early diagnosis of sleep apnea depends on an early recognition of its symptoms. Typical complaints are:
- Excessive daytime sleepiness
- Morning headaches
- Gasping or choking during sleep
- Loud snoring
- Difficulty concentrating
- Irritability or mood changes
- Dry mouth or sore throat in the morning
If you experience these symptoms, you should see a healthcare provider. They can assist in ascertaining whether you suffer from sleep apnea.
Risk factors
Several factors can raise the possibility of sleep apnea development. These risk factors consist of:
- Obesity: Particularly around the neck, extra weight can cause fat buildup that closes the airway during sleep. This obstruction can cause dyspnea.
- Age: Older people are more prone to have sleep apnea. However, the disorder can strike anyone of any ageincluding young adults and children.
- Gender: Men, more often than women, have sleep apnea. After menopause, though, the risk for women rises, underscoring the hormonal factors influencing the disorder.
- Family History: Your risk may be raised by a genetic tendency towards sleep apnea. If sleep apnea runs in your family, you could be more likely to experience it.
- Smoking: Smoking can aggravate the upper airway, raising inflammation and fluid retention. This inflammation can constrict the airways, making sleeping more difficult.
- Certain Medical Conditions: People with particular medical conditions, such as diabetes, heart disease, and high blood pressure, may be more likely to experience sleep apnea. These disorders can aggravate general health risks and the degree of symptoms.
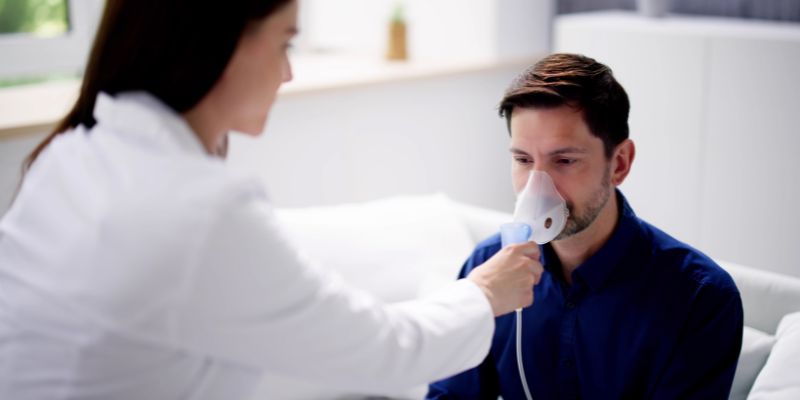

Diagnosis of Sleep Apnea
See a medical provider if you believe you have sleep apnea. To identify the disorder, they might advise a sleep study. Sleep studies mostly fall into two categories:
- Polysomnography (PSG): This overnight sleep study occurs in a sleep lab. It tracks your brain waves, oxygen saturation, heart rate, and breathing patterns.
- Home Sleep Apnea Testing (HSAT): You may do this simplified test at home. It often gauges your oxygen levels and breathing during sleep.
Reviewing the findings, your doctor will decide whether you have sleep apnea. They will also grade the condition's severity.
Sleep Apnea Treatment
The degree and kind of sleep apnea determine the course of treatment. Following are some typical treatment choices:
- Lifestyle Changes: Help comes from losing weight, working out, and avoiding cigarettes. These adjustments might help lessen the severity of sleep apnea.
- Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP): This is a common treatment for OSA. A CPAP machine runs air through a mask, keeping your airway open throughout sleep.
- Oral Appliances: You carry these devices straight in your mouth. By aligning your jaw, they help keep the airway open, lowering the risk of breathing disturbances.
- Surgery: Sometimes, effective treatment of sleep apnea calls for surgery. Surgeons can remove tissue from the throat that might impede breathing or fix structural problems in the airway.
- Positional Therapy: Some people get sleep apnea, mostly when lying on their backs. Your sleeping posture could help ease problems.
- Medications: While no one medicine specifically addresses sleep apnea, some can help control linked conditions, including allergies. These medications can help lower inflammation and improve breathing during sleep, enhancing the general quality of sleep.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, untreated sleep apnea is a major sleep condition with major consequences for health. Early diagnosis depends on realizing its symptoms, which include loud snoring and too much daytime tiredness. There are several forms of sleep apnea; obstructive sleep apnea is the most common. Effective treatment possibilities result from knowing the risk factors and seeing a doctor. Among the available treatments that can enhance general health and sleep quality are lifestyle adjustments, CPAP devices, and dental appliances. Better sleep and improved well-being depend on first giving awareness and control of sleep apnea as a top priority.